Cannabinoids
Cannabinoids are any of a group of closely related compounds which include cannabinol and the active constituents of cannabis.
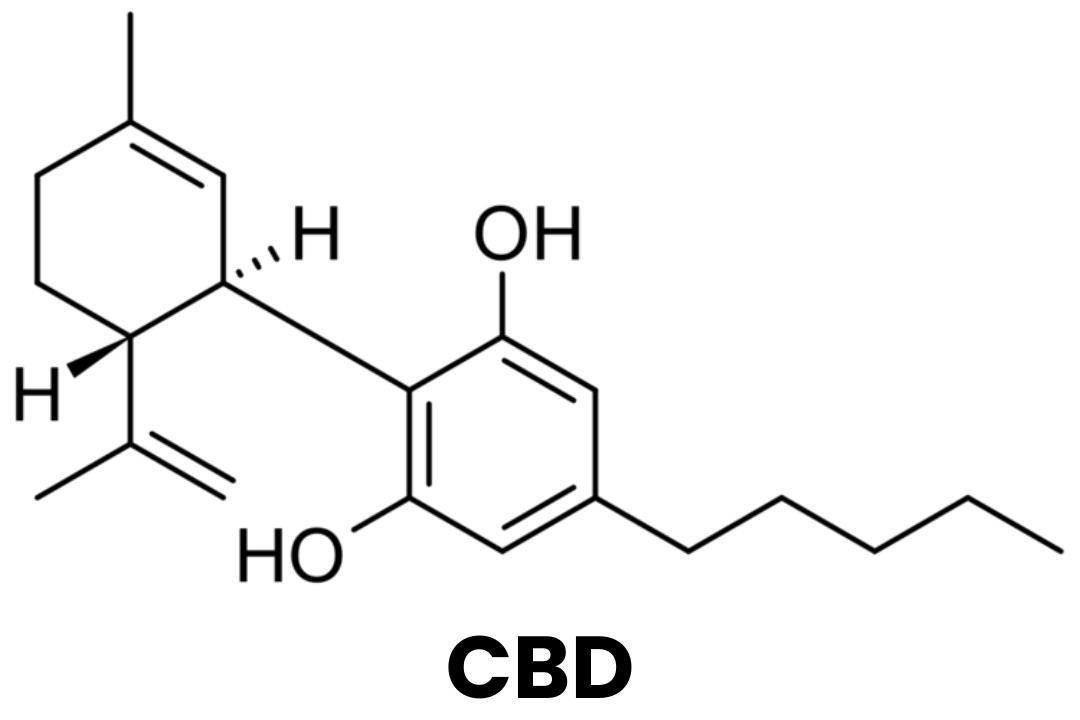
CBD: Cannabidiol, is non-intoxicating and one of 540+ phytochemicals found in the Cannabis sativa (C. sativa) plant. It has increasingly proved its role in easing symptoms of many common health issues.
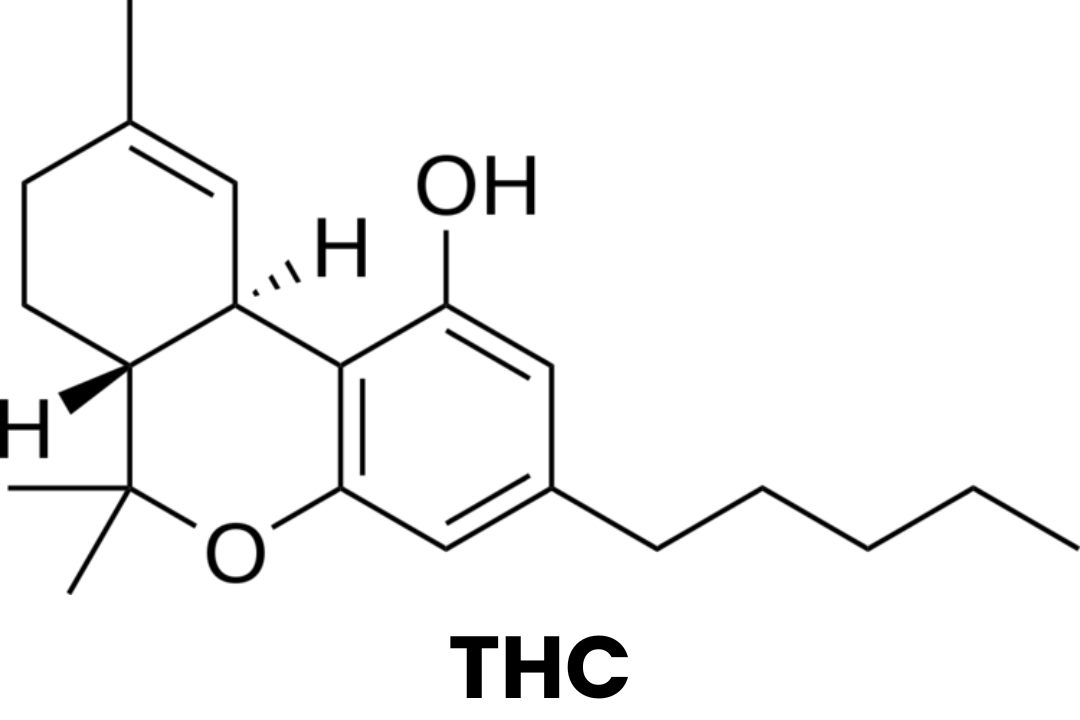
THC: Delta 9/tetrahydrocannabinol is the compound that creates psychotropic effects since they bind to the R1 endocannabinoid receptors in the body. In fact, there are at least two other Delta chains — Delta 8 and Delta 10 — that create psychotropic effects as well, although they derive from hemp not from cannabis. Also, the “high” from D8 and D10 differs greatly from that of D9. It is like the difference between Coca Cola (D9) and Coke Zero (D8/D10). D9 THC continues to be federally illegal even though research has shown it to be beneficial in conjunction with other cannabinoids and terpenes naturally found in the plant.
But there are many other cannabinoids that have been analyzed and researched for their health and wellness benefits. Some examples of the lesser-known cannabinoids:
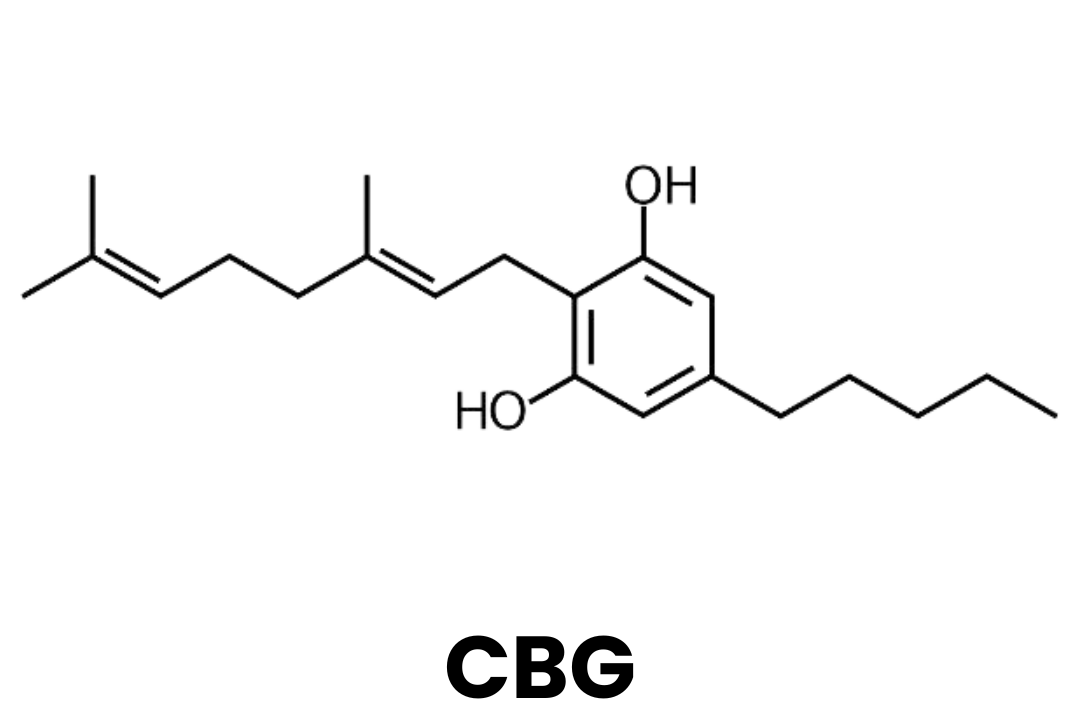
CBG: Cannabigerol is often referred to as the mother of all cannabinoids. This is because other cannabinoids are derived from cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), an acidic form of CBG.
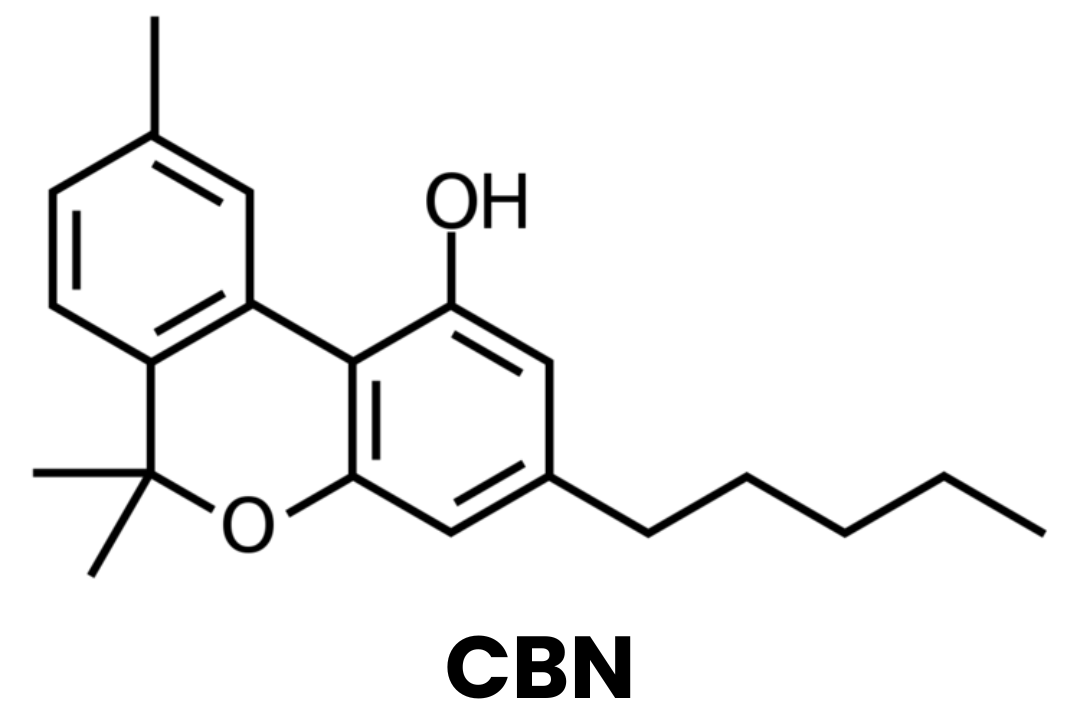
CBN: Cannabinol is created when THC-A oxidizes.
CBC: Cannabichromene has shown effectiveness in a wide variety of medical conditions and their treatments.


